Where does GIS data come from :
- Existing data
- Conversion from existing data
- Creating new data
GIS data are gathered in many ways and some details about data sources are already mentioned in this blog and this is yet again describe the first few phases of GIS process and as we now know that GIS process include Capture, Modelling, Storage , Manipulation and Present are the most important tasks in GIS ,
When gathering data , conversion of old data plays a major role. but those old data are more likely to be in non-digitized form , for example paper maps etc , so how to digitize those data is a challenge.
Digitizing
- Manual Digitizing .
- Automatic Digitizing.
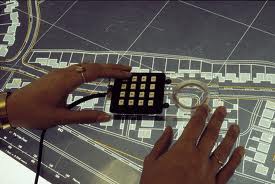
Manual Digitizing
Manual digitizing can be done using digitizing table or by on-screen capturing ,
Digitizing table
First the map is position the map on the table , and then need to set the control points and minimum of 3 control points are needed to get accurate results.features of the map are captured by the cursor.
On-Screen Capturing
GIS software enables this facility, first the map should be scanned and get to a computer , after that using a GIS Capturing software like Arc GIS we can screen capture the maps manually , and can store the digitized data layer by layer , like vegetation layer , buildings layer ... etc
Automatic Digitizing
Manual Digitizing is a vastly time consuming process so comparing to that Automatic method is easy and time saving.and there are scanners for these specialized purposes.in Automatic translation it convert raster to vector by tracing lines in the map and for this should use pattern recognition techniques and algorithms.



.jpg)





.jpg)





.jpg)

